Compare the elements Helium and Tennessine on the basis of their properties, attributes and periodic table facts. Compare elements - Helium and Tennessine comparison table side by side across over 90 properties. All the elements of similar categories show a lot of similarities and differences in their chemical, atomic, physical properties and uses. These similarities and dissimilarities should be known while we study periodic table elements. You can study the detailed comparison between Helium vs Tennessine with most reliable information about their properties, attributes, facts, uses etc. You can compare He vs Ts on more than 90 properties like electronegativity, oxidation state, atomic shells, orbital structure, Electronaffinity, physical states, electrical conductivity and many more. This in-depth comparison helps students, educators, researchers, and science enthusiasts understand the differences and similarities between Helium and Tennessine.
Helium and Tennessine Comparison
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 1 | | | Atomic # Electronic Shell # Symbol Name Atomic Weight Metals | Metalloids | NonMetals | Alkali metals | Alkali earth metals | Lanthanoids | Transition metals | Post-transition metals | Other nonmetals | Halogens | Nobel gas | Actinoids |
| | |
| 2 | | | | | | | | |
| 3 | | | | | | | | |
| 4 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 5 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 6 | | | 57 - 71
La - Lu Lanthanides | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 7 | | | 89 - 103
Ac - Lr Actinides | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lanthanides | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Actinides | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Here's a detailed comparison between Helium (He) and Tennessine (Ts), focusing on their position in the periodic table, physical and chemical properties, stability, and uses.
Facts - Basic Element Details
History
| Parameter | Helium | Tennessine |
|---|
| History | The element Helium was discovered by P. Janssen and N. Lockyer in year 1868 in Sweden and United Kingdom. Helium derived its name from the Greek word helios, meaning 'sun'. | The element Tennessine was discovered by Yuri Oganessian et al.(JINR in Dubna) in year 2010. Tennessine derived its name from Tennessee, United States. |
| Discovery | P. Janssen and N. Lockyer (1868) | Yuri Oganessian et al.(JINR in Dubna) (2010) |
| Isolated | W. Ramsay,T. Cleve, and N. Langlet (1895) | () |
Presence: Abundance in Nature and Around Us
Parts per billion (ppb) by weight / by atoms (1ppb =10^-7 %)
Crystal Structure and Atomic Structure
Atomic and Orbital Properties
| Property | Helium | Tennessine |
|---|
| Atomic Number | 2 | 117 |
| Number of Electrons (with no charge) | 2 | 117 |
| Number of Protons | 2 | 117 |
| Mass Number | 4.002602 | 294 |
| Number of Neutrons | 2 | 177 |
| Shell structure (Electrons per energy level) | 2 | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 7 |
| Electron Configuration | 1s2 | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p5 |
| Valence Electrons | 1s2 | 7s2 7p5 |
| Oxidation State | - | - |
| Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) | 1S0 | 2P3/2 |
| Shell structure | 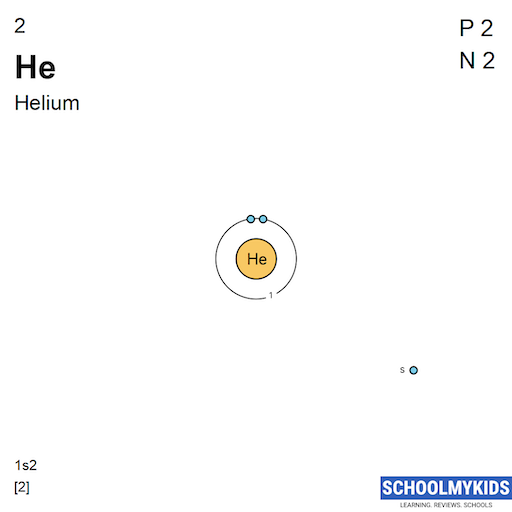 | 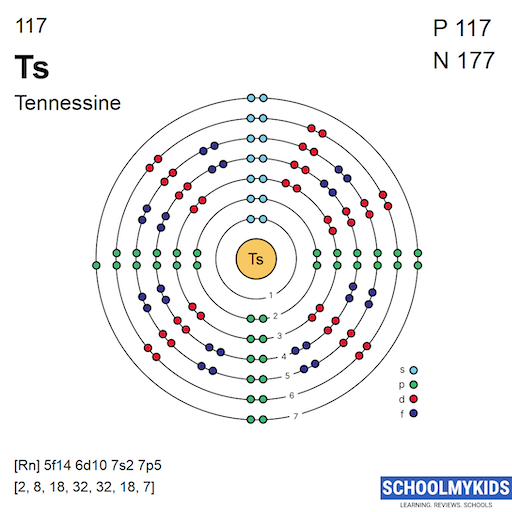 |
Isotopes and Nuclear Properties
Helium has 2 stable naturally occuring isotopes while Tennessine has 0 stable naturally occuring isotopes.
Chemical Properties: Ionization Energies and electron affinity
Physical Properties
| Property | Helium | Tennessine |
|---|
| Phase at STP | Gas | Solid |
| Color | Colorless | - |
| Density | 0.0001785 g/cm3 | - |
| Density (when liquid (at melting point)) | - | - |
| Molar Volume | 22.4136 cm3/mol | - |
Mechanical and Hardness Properties
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Magnetic and Optical Properties
Thermal Properties - Enthalpies and thermodynamics
Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
Compare Helium and Tennessine With Other Elements
Compare Helium and Tennessine with other elements of the periodic table. Explore howHelium and Tennessine stack up against other elements of the periodic table. Use our interactive comparison tool to analyze 90+ properties across different metals, non-metals, metalloids, and noble gases. Understanding these differences is crucial for applications in engineering, chemistry, electronics, biology, and material science.
Compare Helium with all Group 18 elementsCompare Helium with all Period 1 elementsCompare Helium with all Noble Gas elements | Compare Tennessine with all Group 17 elementsCompare Tennessine with all Period 7 elementsCompare Tennessine with all Halogens elements |